Sustainable Urban Development: Building Greener Cities for the Future

Introduction:
As urbanization continues to accelerate, cities around the world face the dual challenge of accommodating growing populations while minimizing environmental impact. By 2050, nearly 70% of the global population is expected to live in urban areas, placing immense pressure on infrastructure, resources, and ecosystems. Sustainable urban development offers a transformative approach to addressing these challenges, focusing on creating cities that are environmentally friendly, economically viable, and socially inclusive.
Sustainable urban development encompasses a wide range of strategies, including energy-efficient buildings, green transportation systems, and the integration of green spaces to improve air quality and biodiversity. It also involves the use of smart technologies to optimize resource use and reduce emissions, ensuring that cities can grow without compromising the planet’s future.
This shift toward greener cities is not just about mitigating climate change—it’s about creating urban environments where people can thrive. From enhancing public health to fostering economic opportunities, sustainable urban development holds the key to a more resilient and equitable future. In this blog, we will explore the principles, benefits, and innovative practices driving the transformation of urban landscapes worldwide.
1. The Principles of Sustainable Urban Development
Sustainable urban development is built upon foundational principles that aim to harmonize environmental health, social well-being, and economic growth. Environmental stewardship is a critical aspect of this, requiring cities to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, conserve resources, and integrate nature into urban design. Efforts such as planting urban forests, managing water responsibly, and adopting renewable energy sources are examples of how cities can prioritize sustainability. Green infrastructure—such as bioswales and green roofs—also plays a role in improving water management and enhancing biodiversity within densely populated areas.
Social equity underpins sustainable urban development by ensuring that urban benefits are accessible to all citizens, regardless of income or background. Inclusive housing policies, equitable access to public transportation, and participatory urban planning processes empower communities and address systemic inequalities. Economic resilience complements these efforts by promoting green jobs, supporting local businesses, and encouraging innovation through circular economy practices. Together, these principles provide a comprehensive framework for cities to address current challenges while building a sustainable future.
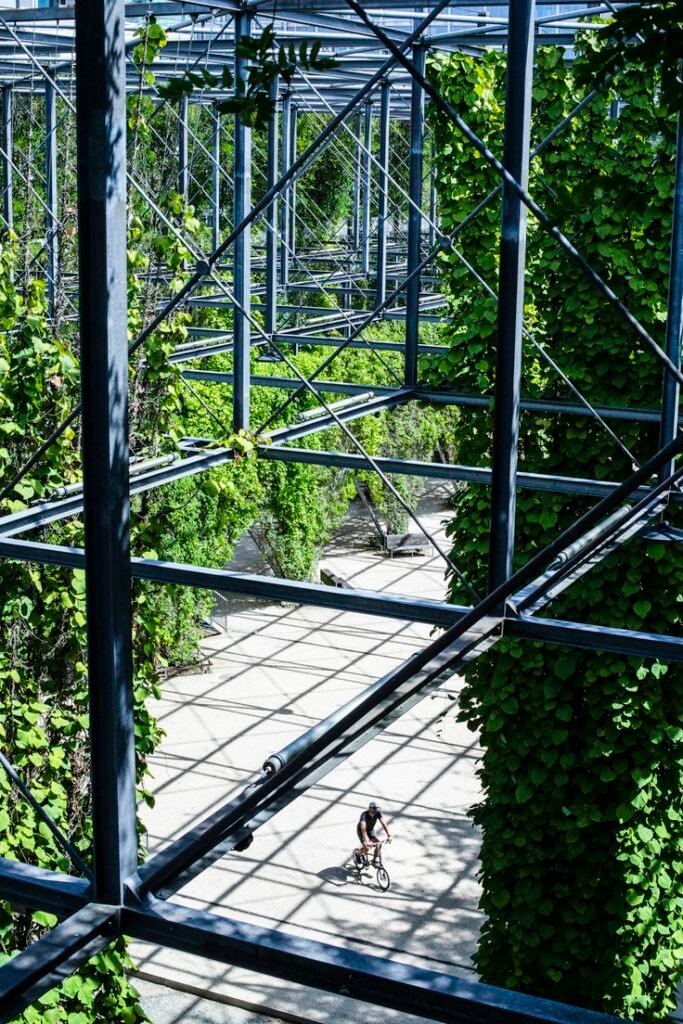

2. Energy-Efficient Building and Design
The built environment is one of the largest contributors to energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, making energy-efficient construction a cornerstone of sustainable urban development. Modern green architecture leverages materials and technologies that reduce energy demand, such as high-performance insulation, energy-efficient windows, and solar panels. Buildings designed to generate more energy than they consume—known as net-zero energy buildings—are becoming increasingly prevalent in forward-thinking cities. Passive design principles, which maximize natural light and ventilation, further reduce energy usage while enhancing indoor comfort.
Retrofitting existing buildings offers a practical solution for improving urban sustainability without extensive new construction. Adding renewable energy systems, upgrading lighting to LED, and incorporating smart building technologies enable older structures to meet modern efficiency standards. Smart buildings equipped with sensors and automated systems can monitor and adjust energy use in real-time, reducing waste and lowering costs. These advancements highlight the potential of both new and existing buildings to minimize their environmental impact while providing economic and social benefits.

3. Sustainable Transportation Systems
Transportation is a key area where urban development intersects with sustainability goals. Many cities are investing in public transportation systems such as metro networks, electric buses, and light rail to provide reliable and eco-friendly alternatives to private vehicles. By reducing traffic congestion and emissions, these systems contribute to cleaner air and a healthier urban environment. Cities like Copenhagen and Amsterdam serve as models for integrating active transportation options, with extensive bike lanes and pedestrian-friendly pathways that encourage walking and cycling.
Emerging technologies are also reshaping urban mobility. Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more common, supported by expanding charging infrastructure that makes adoption easier for consumers. Autonomous vehicles, still in development, promise to further revolutionize urban transportation by improving safety and reducing congestion. Ride-sharing platforms, carpooling programs, and micro-mobility solutions like e-scooters and bike-sharing schemes are additional examples of how technology is providing sustainable alternatives to traditional transportation modes. Together, these initiatives help reduce the carbon footprint of urban travel while improving connectivity and quality of life for city dwellers.
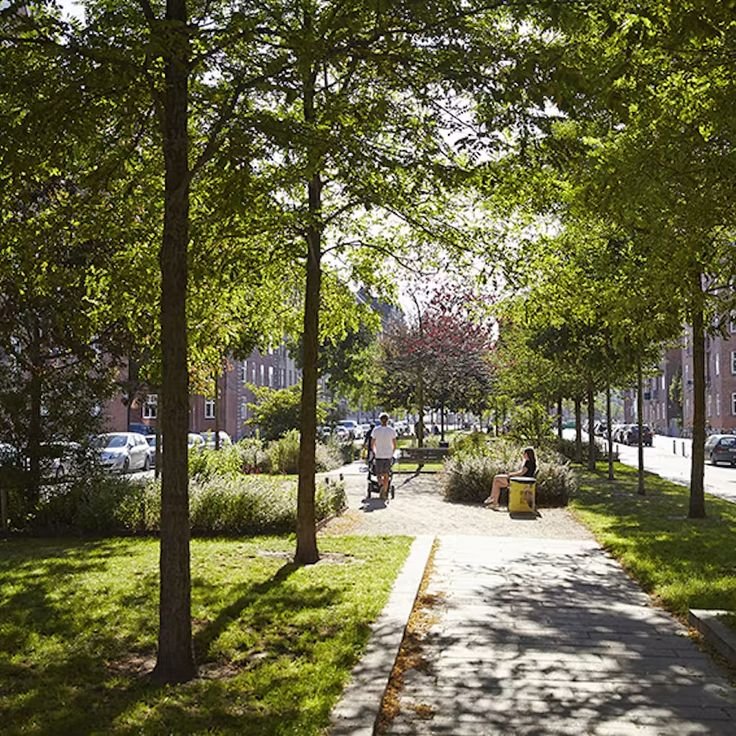
4. Green Spaces and Urban Biodiversity
Green spaces are vital components of sustainable cities, offering environmental, social, and health benefits that enhance urban life. Parks, green roofs, and community gardens provide recreational areas that promote physical activity and mental well-being while improving air quality and regulating urban temperatures. In dense urban areas, vertical gardens and pocket parks offer creative solutions to integrating greenery into limited spaces, helping to combat the urban heat island effect.
Biodiversity is another crucial aspect of green urban design. Initiatives like wildlife corridors and native plant landscaping create habitats for local fauna, fostering a harmonious coexistence between nature and city life. Urban agriculture projects, such as rooftop farms and community gardens, not only contribute to food security but also strengthen community ties and increase environmental awareness. By prioritizing green spaces and biodiversity, cities can enhance resilience to climate impacts while creating vibrant, livable environments for their residents.

5. The Role of Smart Technologies
Smart technologies are revolutionizing urban management by making cities more efficient, adaptable, and sustainable. Smart grids enable the seamless integration of renewable energy sources into the electricity supply, reducing waste and optimizing energy use. Advanced waste management systems equipped with IoT sensors can track collection needs, improve recycling rates, and reduce landfill contributions. These innovations ensure that resources are used effectively, benefiting both the environment and urban economies.
Data analytics is another powerful tool in sustainable urban development. Real-time monitoring of air quality, traffic patterns, and energy consumption helps city planners make informed decisions and address challenges proactively. For example, smart traffic systems can optimize signal timings to reduce congestion and emissions, while environmental sensors provide critical insights into pollution hotspots. By harnessing the capabilities of smart technologies, cities can transition toward a more sustainable and interconnected future, where resources are managed with precision and care.
Conclusion:
Sustainable urban development is no longer an option but a necessity for addressing the environmental, social, and economic challenges of urbanization. By embracing principles of environmental stewardship, social equity, and economic resilience, cities can evolve into vibrant, sustainable hubs where people and nature thrive together.
Through energy-efficient building designs, sustainable transportation systems, green spaces, and smart technologies, urban areas can minimize their environmental impact while enhancing quality of life. However, achieving these goals requires collaboration among governments, businesses, and communities to implement innovative solutions and foster a culture of sustainability.
The journey toward greener cities is a shared responsibility and an opportunity to shape a future that balances progress with preservation. Together, we can build urban environments that are resilient, inclusive, and sustainable for generations to come.